Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor incorporating the functions of a computers central processing unit (CPU) on a single integrated circuit (IC or chip), or at most a few integrated circuits.
It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions in its memory, and provides results as output. Its an example of sequential digital logic, as it has internal memory.
Microprocessors operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary numeral system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few chips greatly reduced the cost of processing power.
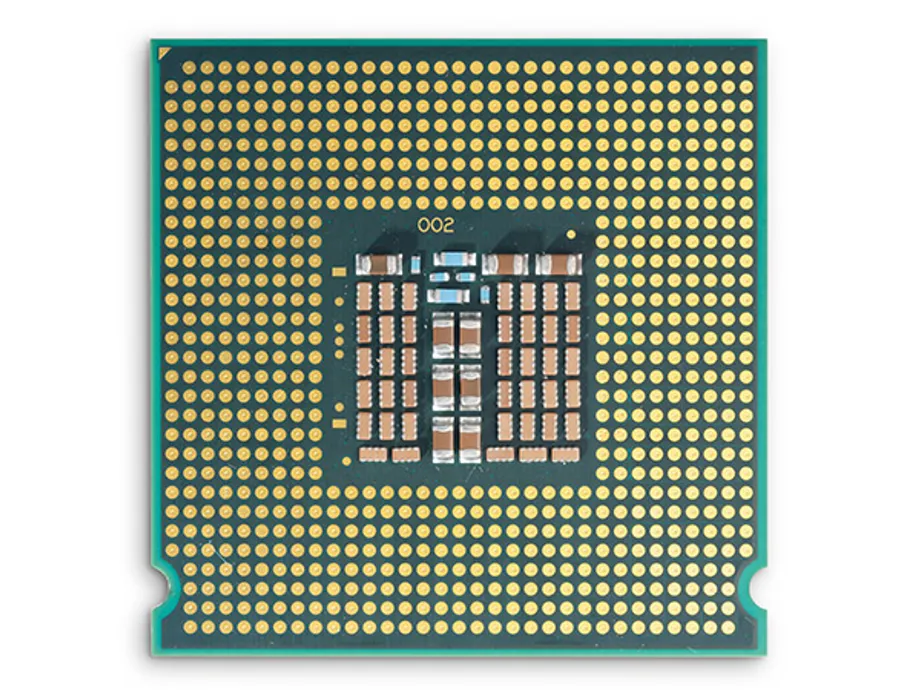
2 Intel chips
The two microprocessors or chips shown here are Intels Xeon processor number E5430 which have a 12MB cache and a processor base frequency of 2.66 GHz. Intel Corporation, founded in July 1968, is an American multinational technology company, headquartered in Santa Clara, California.
Intel= is one of the worlds largest chipmakers and is the inventor of the x86 series of microprocessors found in most personal computers. Intel created the worlds first commercial microprocessor chip in 1971, but it was not until the success of the personal computer that this became its primary business.